The average ORM agency wastes 15-20 hours per week having junior staff manually search for companies with reputation crises. They scan Google results, monitor news alerts, and browse review sites hoping to catch businesses at their most vulnerable moment – when negative coverage threatens their bottom line.
This scattershot approach misses opportunities, burns resources, and delivers inconsistent results. While your team manually researches 50 companies per week, hundreds of businesses face reputation emergencies that could become high-value retainer clients.
The solution is to use an integrated system such as Jolly Reputation Radar. It continuously detects harmful branded visibility, applies urgency scoring, enriches company and contact data, and synchronizes this information with existing CRM and outreach workflows.
Jolly Reputation Radar removes the need for manual research. It systematically identifies companies facing negative search results, critical press coverage, review anomalies, or Wikipedia controversies. The system operates continuously and provides your team with structured, qualified information about companies with acute ORM needs.
For established ORM agencies, this approach transforms business development from reactive to proactive. You reach prospects during their moment of highest pain, when they’re actively seeking reputation management solutions. The result is shorter sales cycles, higher conversion rates, and predictable pipeline growth that scales beyond your current research capacity.
Contents
- 1 The Manual Research Trap
- 2 What Counts as Harmful Online Visibility?
- 3 Inside the Automated System
- 4 Build vs Buy: Why Automation Wins
- 5 How to Measure ROI
- 6 Case Example: From Detection to Retainer
- 7 FAQ
- 7.1 How do you define harmful online visibility?
- 7.2 How frequently does the automated detection run?
- 7.3 Which sources are covered by the detection system?
- 7.4 How do you reduce false positives in reputation monitoring?
- 7.5 What CRM and outreach integrations are available?
- 7.6 How does the system handle GDPR and privacy compliance?
The Manual Research Trap
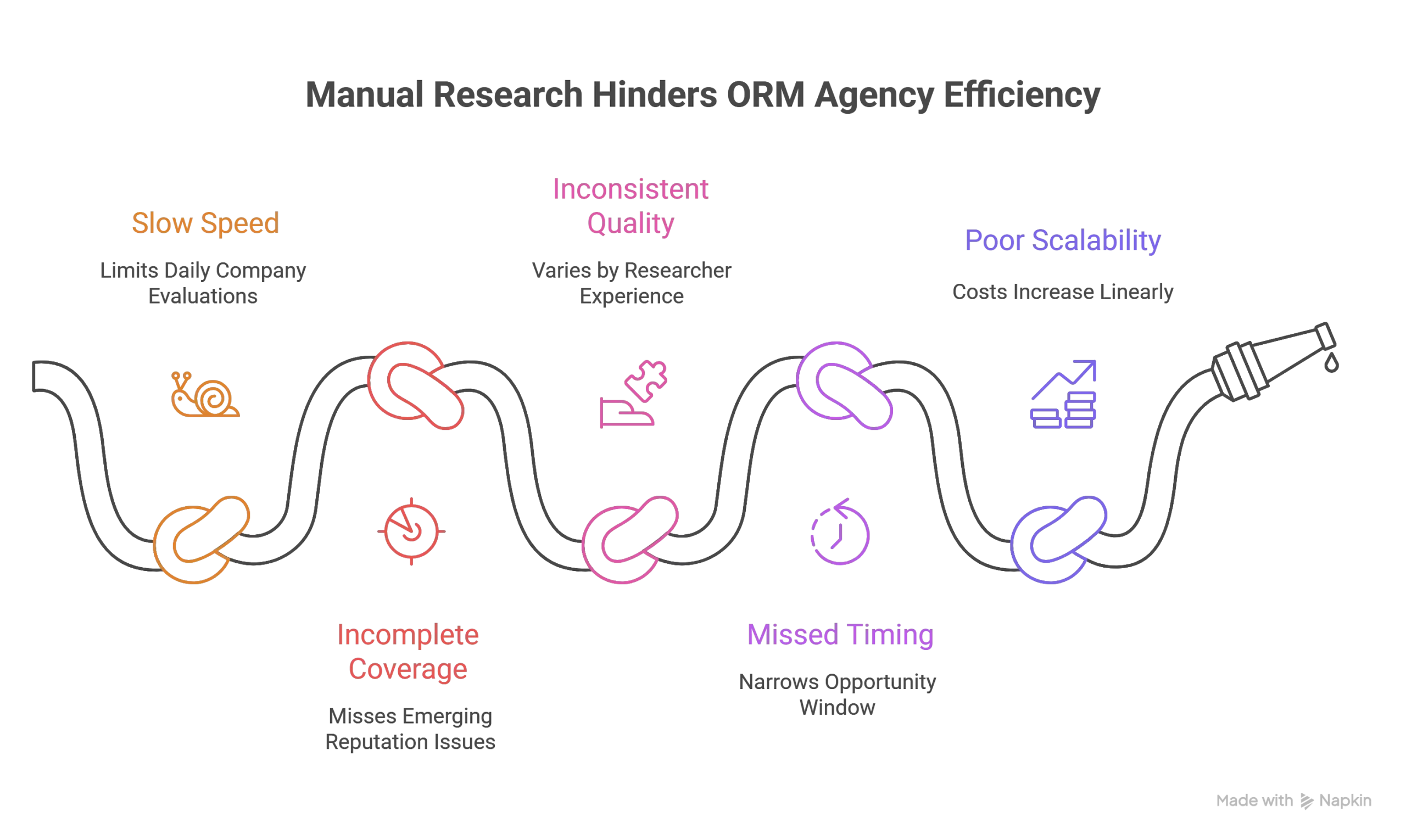
Most ORM agencies rely on junior staff or interns to manually identify prospects with reputation problems. The typical process involves googling company names with negative keywords, setting up Google Alerts for industry terms, browsing review sites like Glassdoor or Trustpilot, and scanning trade publications for crisis coverage.
This manual approach creates several critical problems. First, it’s impossibly slow and resource-intensive. A junior researcher might evaluate 20-30 companies per day, requiring significant time to assess each situation’s severity and business impact. Second, the coverage is sporadic and incomplete. Human researchers can’t monitor thousands of companies simultaneously or catch reputation issues the moment they emerge.
The quality problem is equally damaging. Manual research produces inconsistent results depending on the researcher’s experience and methodology. One person might flag minor review fluctuations while missing serious regulatory investigations. Another might focus heavily on news coverage while overlooking devastating first-page search results.
Timing represents the biggest missed opportunity. By the time manual research identifies a reputation crisis, the company has likely already begun addressing the issue internally or engaged competing agencies. The window for positioning your agency as the solution provider has narrowed significantly.
Finally, manual research doesn’t scale with agency growth. Adding more researchers increases costs linearly while maintaining the same quality and speed limitations. There’s no leverage or efficiency gain – just proportionally higher overhead for marginally better coverage.
What Counts as Harmful Online Visibility?
Effective online reputation monitoring for agencies requires understanding which visibility patterns indicate genuine business threats versus minor public relations noise. Harmful visibility falls into several distinct categories, each representing different levels of commercial risk.
Negative keyword associations represent the most direct threat. When searches for a company name return results containing terms like “scam,” “fraud,” “lawsuit,” “investigation,” or “bankruptcy,” the reputational damage is immediate and measurable. These associations appear in search suggestions, knowledge panels, and organic results, directly influencing prospect and customer perceptions.
Branded search crisis scenarios occur when negative content dominates the first page of search results for a company’s name. This might include unfavorable news articles, regulatory filings, competitor attack sites, or employee complaints. The positioning and authority of these negative results determines their business impact.
Review platform spikes indicate systematic reputation attacks or genuine service failures. A sudden influx of one-star reviews, especially with similar language patterns, suggests either coordinated negative campaigns or widespread customer dissatisfaction requiring immediate attention.
Wikipedia controversies carry unique weight due to the platform’s authority and prominent search positioning. Negative Wikipedia sections about companies or their executives can persist for years, influencing every subsequent branded search.
Social media amplification transforms isolated incidents into widespread reputation threats. When negative content gains traction across multiple social platforms, the velocity and reach create urgency that traditional PR approaches cannot address quickly enough.
These harmful visibility patterns translate directly into business consequences: reduced organic search traffic, lower conversion rates on branded campaigns, decreased investor confidence, talent acquisition challenges, and customer churn. Companies experiencing these issues become ideal prospects for specialized ORM interventions.
Inside the Automated System
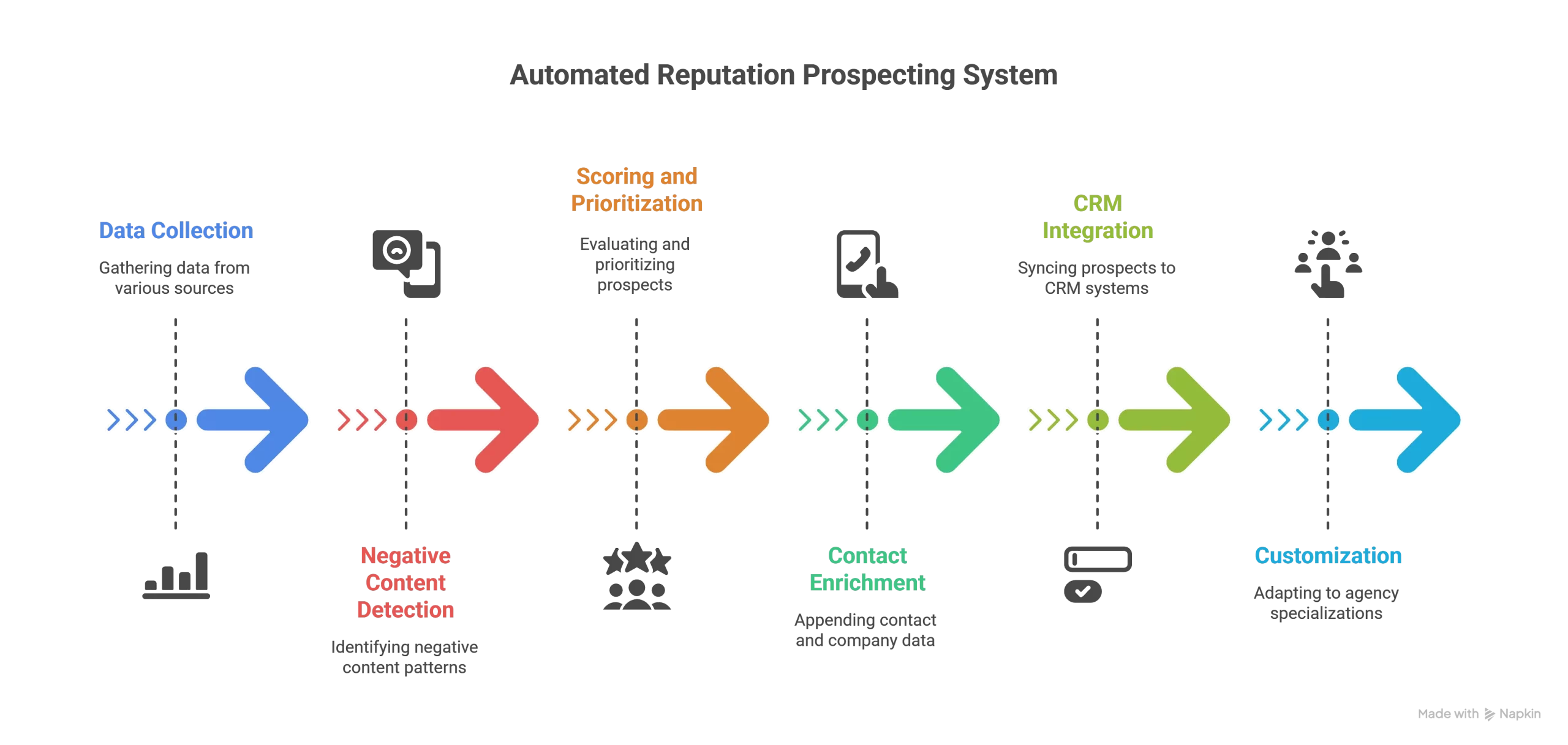
The automated reputation prospecting system operates through five integrated components that work continuously to identify and qualify ORM prospects without manual intervention.
Detection and Data Collection
The system begins with comprehensive data inputs defining your ideal prospect profile. You configure target keywords, geographic markets, company size ranges, and industry verticals. The detection engine then monitors multiple data sources simultaneously: Google search results for branded queries, news publications and trade media, review platforms including Glassdoor, Trustpilot, and Yelp, social media mentions across major platforms, and Wikipedia entries and edits.
Unlike generic monitoring tools, Jolly Reputation Radar is designed to detect negative visibility patterns relevant to ORM. It highlights harmful keyword associations, sudden review rating declines, critical press coverage, and shifts in search result positioning that signal potential reputation problems.
Intelligent Scoring and Prioritization
Raw detection data feeds into a sophisticated scoring algorithm that evaluates multiple factors to determine prospect priority. Severity scoring analyzes the nature of negative content – fraud allegations score higher than minor service complaints. Recency weighting prioritizes fresh reputation issues when companies are most likely to seek immediate help.
Authority assessment considers the credibility and reach of sources publishing negative content. Coverage in major publications receives higher scores than obscure blog posts. Visibility measurement evaluates where negative content appears in search results, with first-page positioning receiving maximum priority scores.
The system also incorporates velocity tracking, identifying situations where reputation issues are accelerating rather than isolated incidents. This multifactor approach ensures your sales team focuses on prospects with both significant reputation problems and realistic closure probability.
Contact Enrichment and Intelligence
Once the system identifies qualified reputation prospects, automated enrichment appends crucial contact and company data. This includes decision-maker contact information, company firmographics, recent funding or growth indicators, and existing agency relationships where detectable.
The enrichment process specifically targets roles most likely to own reputation management decisions: CMOs, brand managers, communications directors, and C-level executives. For each contact, the system attempts to gather direct email addresses, LinkedIn profiles, and phone numbers where appropriate.
CRM Integration and Routing
Qualified prospects automatically sync to your existing sales infrastructure. Jolly Reputation Radar integrates directly with established CRMs such as HubSpot, Salesforce, and Pipedrive. Each record contains structured context about the detected reputation issue, enabling informed follow-up without extra manual research.
Each prospect record includes the original negative content, severity scores, contact data, and suggested messaging angles. This enables immediate, informed outreach without requiring additional research from your sales team.
Flexibility and Customization
The automated system adapts to different agency specializations and market approaches. Agencies focused on executive reputation can emphasize Wikipedia and news monitoring. Those targeting local businesses might prioritize review platform detection. Crisis communications specialists can configure alerts for breaking news and regulatory filings.
Exclusion filters prevent false positives by removing your existing clients, companies in irrelevant industries, and sources known for unreliable content. The system learns from your feedback, improving accuracy and relevance over time.
Build vs Buy: Why Automation Wins
ORM agencies typically choose between manual research, monitoring tool subscriptions, or automated prospecting systems. Each approach offers different advantages and limitations that directly impact agency growth potential.
Manual research provides maximum flexibility and human judgment but suffers from speed and scale constraints. Even experienced researchers can only evaluate a limited number of prospects daily, and the quality depends heavily on individual skills and attention levels. Costs scale linearly with coverage requirements, making comprehensive market monitoring economically unfeasible.
Traditional monitoring tools like Mention, Brand24, or Meltwater offer broad coverage but lack ORM-specific focus. These platforms track general brand mentions rather than specifically identifying reputation crises. They generate significant noise requiring manual filtering and rarely provide contact enrichment for identified opportunities.
Enterprise tools like Cision or Meltwater provide excellent media monitoring but focus on PR professionals and journalists rather than prospecting capabilities. They excel at tracking coverage but don’t translate findings into sales opportunities.
SEO tools such as SEMrush or Ahrefs monitor search rankings and visibility changes but miss non-SEO reputation issues like review problems or social media crises. Their business intelligence features target marketing teams rather than ORM-specific use cases.
Automated prospecting systems specifically designed for detect negative search results combine the comprehensiveness of monitoring tools with the business intelligence of manual research. They operate continuously without increasing headcount, focus specifically on ORM-relevant reputation issues, and deliver pre-qualified prospects ready for immediate outreach.
The cost structure favors automation significantly. Manual research costs $40,000-60,000 annually per researcher while providing limited coverage. Monitoring tool subscriptions range from $500-5,000 monthly but require additional staff time for analysis and follow-up. Automated systems typically cost less than a single researcher while delivering superior coverage and qualification.
How to Measure ROI
Measuring the effectiveness of automated reputation management prospecting requires tracking both leading and lagging indicators that demonstrate system performance and business impact.
Leading Indicators
Leading indicators measure system output and operational efficiency. Qualified accounts detected per week shows whether your targeting parameters effectively identify relevant prospects. Severity score distribution indicates if the system catches both minor issues and major crises appropriately.
Source coverage metrics reveal which data sources produce the highest-quality prospects, enabling optimization of detection parameters. Time from detection to outreach measures how quickly your team acts on fresh opportunities when prospects are most receptive.
Contact enrichment success rates determine data quality and outreach feasibility. Higher enrichment rates directly correlate with outreach capacity and conversion potential.
Lagging Indicators
Lagging indicators measure business outcomes and revenue impact. Meeting conversion rates from automated prospects versus manual research quantifies prospecting quality improvements. Average deal size from automated leads often exceeds manual research results because the system identifies more severe reputation crises.
Sales cycle length typically decreases with automated prospecting because timing improves significantly. Reaching prospects during active reputation crises reduces the educational and urgency-building phases of traditional ORM sales processes.
Monthly recurring revenue from automated prospecting clients provides the ultimate ROI measurement. Track both initial retainer values and account expansion over time.
ROI Calculation Example
Consider an agency spending $50,000 annually on manual research producing 20 qualified prospects monthly with a 15% meeting conversion rate and 25% close rate. This generates approximately 9 new clients annually.
An automated system costing $30,000 annually might identify 100 qualified prospects monthly with a 25% meeting conversion rate and 35% close rate, producing roughly 105 new clients annually.
The automation delivers 10x more prospects, higher conversion rates at multiple funnel stages, and net cost savings of $20,000. Even accounting for reduced average deal size, the ROI improvement is substantial and compounds as the system learns and improves targeting accuracy.
Case Example: From Detection to Retainer
A mid-sized technology company triggered the automated system when negative glassdoor reviews spiked following a layoff announcement, while simultaneously facing a Wikipedia vandalism attack that added unfounded fraud allegations to their company page.
Day 0: Detection and Scoring
The system detected both reputation threats within hours. Glassdoor reviews mentioning “toxic culture” and “unethical practices” scored moderately for severity but highly for velocity due to the sudden increase. The Wikipedia vandalism scored maximally due to the fraud allegations and high search visibility.
Automated enrichment identified the CMO and VP of Communications as primary contacts, gathering direct email addresses and recent LinkedIn activity showing concern about company culture communications.
Day 1: Targeted Outreach
The sales team received a complete prospect profile including screenshots of negative content, severity scores, and contact data. Their initial outreach referenced the specific Wikipedia issue and offered immediate help with emergency reputation triage.
The email achieved a response within four hours because timing was perfect – the executive team was actively discussing reputation management options following the crisis emergence.
Day 4: Qualified Meeting
The discovery call revealed the company was indeed seeking emergency reputation management support. The Wikipedia vandalism was affecting partnership discussions, while the Glassdoor issues were complicating recruitment efforts.
Because the outreach occurred during the active crisis rather than weeks later, the agency positioned itself as the immediate solution rather than competing against established relationships or internal initiatives.
Result: Six-Figure Retainer
The company signed a comprehensive reputation management retainer within two weeks, including Wikipedia monitoring, review management, and crisis communications support. The total contract value exceeded $150,000 annually.
This outcome was only possible because automation detected the reputation crisis immediately, provided complete context for informed outreach, and enabled contact during the peak urgency window when executives were most receptive to external reputation management support.
Jolly Reputation Radar shifts ORM prospecting from reactive research to structured, proactive identification. It provides agencies with timely, contextualized insights into companies experiencing acute reputation management needs.
FAQ
How do you define harmful online visibility?
Harmful online visibility includes any content that damages a company’s reputation when prospects or customers search for their brand name. This encompasses negative search results on the first two pages of Google, unfavorable news coverage from credible sources, sudden spikes in negative reviews, Wikipedia controversies, and social media content that associates the brand with negative keywords like fraud, scam, or lawsuit.
How frequently does the automated detection run?
The system operates continuously with real-time monitoring capabilities, but practical detection cycles run daily for most sources. Search result changes are detected within 24 hours, news coverage monitoring updates every few hours, and social media scanning occurs in near real-time. Review platforms are monitored daily due to their update frequency.
Which sources are covered by the detection system?
Coverage includes Google search results for branded queries, major news publications and trade media, review platforms such as Glassdoor, Trustpilot, Yelp, and industry-specific sites, social media platforms including Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook, Wikipedia entries and edit histories, regulatory filing databases, and court record systems where publicly available.
How do you reduce false positives in reputation monitoring?
False positive reduction involves multiple filtering layers including domain exclusions for known competitors or irrelevant sites, keyword context analysis to distinguish between negative mentions and neutral usage, source credibility scoring to prioritize authoritative content, and machine learning algorithms that improve accuracy based on agency feedback about prospect quality and relevance.
What CRM and outreach integrations are available?
The system integrates directly with popular sales platforms including HubSpot, Salesforce, Pipedrive, etc. as well as Clay.com for contact enrichment, Smartlead and similar outreach platforms, and Zapier/Make.com/N8N for custom workflow connections. Integration typically syncs prospect data, reputation context, severity scores, and enriched contact information automatically.
How does the system handle GDPR and privacy compliance?
All contact data enrichment uses publicly available information sources and complies with GDPR requirements for business contact processing. The system includes opt-out mechanisms, data retention controls, and processing justification based on legitimate business interests for B2B prospecting activities within regulatory guidelines.