The traditional cost-plus pricing model that dominated SaaS for decades is experiencing a seismic shift, with research revealing that companies implementing value based pricing saas strategies achieve returns that dwarf conventional optimization efforts. McKinsey’s latest analysis shows that pricing optimization impacts profitability four times more effectively than cost-cutting measures, yet only 46% of SaaS companies have moved beyond simplistic per-user models. This disconnect between pricing potential and actual implementation represents billions in unrealized revenue across the industry. The data becomes even more striking when considering that 42% of tracked SaaS providers adjusted their pricing in 2024’s first three quarters, with average increases hitting 20% – signaling an industry-wide awakening to the power of strategic pricing.
As companies scramble to maintain growth amid 8.7% year-over-year SaaS price inflation and organizations spending $7,900 per employee annually on software tools, the shift from cost-based pricing to value-oriented models isn’t just strategic – it’s existential for maintaining competitive advantage in an increasingly sophisticated market.
Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Understanding Value-Based Pricing in Today’s SaaS Market
- 3 Current Market Trends and Pricing Statistics
- 4 Benefits and Competitive Advantages of Value-Based Pricing
- 5 Implementation Framework and Best Practices
- 6 Value Metrics and Measurement Strategies
- 7 Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Key Takeaways
- Companies using value-based pricing achieve 15-20% higher retention rates and 10-15% contract value increases
- Usage-based models show 29.9% five-year CAGR, significantly outpacing traditional subscription growth
- Hybrid pricing models combining multiple value metrics deliver 30% better retention than single-metric approaches
- Van Westendorp analysis implementation drives 14% average expansion revenue increases
- 42% of SaaS companies updated pricing in 2024 with 20% average increases, signaling market-wide pricing evolution
Understanding Value-Based Pricing in Today’s SaaS Market
Value-based pricing for SaaS fundamentally redefines how software companies monetize their products by anchoring prices to customer-perceived value rather than internal costs or competitor benchmarks. This approach represents a philosophical shift from traditional pricing models that focus on production expenses plus desired margins. The distinction becomes clear when examining implementation: while cost-plus models calculate prices based on development costs and overhead, value-based strategies derive pricing from measurable customer outcomes and business impact.
The current market landscape reveals an industry in transition, with 54% of SaaS vendors still clinging to per-user pricing despite mounting evidence of its limitations. Usage-based pricing captures 26% of the market, while hybrid models combining multiple approaches account for the remaining 20%. This distribution masks significant momentum shifts – usage-based models have achieved a remarkable 29.9% five-year compound annual growth rate, nearly triple the broader SaaS market’s expansion pace.
Strategic pricing decisions have taken on unprecedented importance as growth rates normalize from pandemic-era highs. The compound annual growth rate for B2B SaaS has stabilized at 12.2% in 2024’s first half, down from nearly 50% in early 2022. This deceleration forces companies to extract more value from existing customers rather than relying solely on new acquisition. The response has been dramatic: 42 companies in a tracked index updated their pricing two or more times per quarter, demonstrating that iterative pricing strategies have become the new normal.
The Evolution from Static to Dynamic Pricing Models
Traditional subscription models operated on simplicity – set a price, charge monthly or annually, and hope for renewal. This approach worked when SaaS was novel and customers had limited alternatives. Today’s buyers demand pricing that reflects their actual usage patterns and value realization. The shift mirrors broader changes in how businesses consume technology, moving from fixed capacity planning to elastic consumption models that scale with needs.
Customer expectations have evolved dramatically, with nearly 80% of SaaS companies planning to leverage usage data for pricing personalization. This data-driven approach enables pricing that adapts to individual customer behavior patterns, creating fairness perceptions that strengthen retention. Companies ignoring this trend risk competitive disadvantage as customers increasingly expect pricing transparency and alignment with their success metrics.
Current Market Trends and Pricing Statistics
The SaaS pricing environment in 2024 reflects unprecedented inflationary pressures combined with customer demands for greater value demonstration. Year-over-year price inflation for SaaS products sits at 8.7%, forcing procurement teams to scrutinize every subscription renewal. This inflation directly impacts IT budgets, with companies now allocating $7,900 per employee annually to SaaS tools – a 27% increase over the past two years that strains operational budgets.
Market dynamics reveal that approximately 50% of software companies plan to raise prices and reduce discounts in coming months, according to McKinsey research. This coordinated move toward higher pricing reflects both inflationary pressures and recognition that many SaaS products have been systematically underpriced relative to delivered value. The shift requires careful orchestration to avoid customer backlash while capturing fair value for solutions that often deliver transformative business outcomes.
The Data-Driven Pricing Revolution
Modern SaaS companies increasingly rely on sophisticated analytics to inform pricing decisions. Product telemetry data reveals feature usage patterns, customer engagement levels, and value realization indicators that guide pricing optimization. Companies analyzing this data discover that customers using certain feature combinations show higher retention rates and willingness to pay premium prices, enabling targeted pricing strategies that maximize revenue while maintaining satisfaction.
The sophistication of pricing analytics has evolved from simple cohort analysis to machine learning models that predict price elasticity at the individual customer level. Advanced companies now employ dynamic pricing algorithms that adjust offers based on customer characteristics, usage patterns, and competitive alternatives. This granular approach to pricing enables revenue optimization that would have been impossible with traditional fixed-tier models.
Benefits and Competitive Advantages of Value-Based Pricing
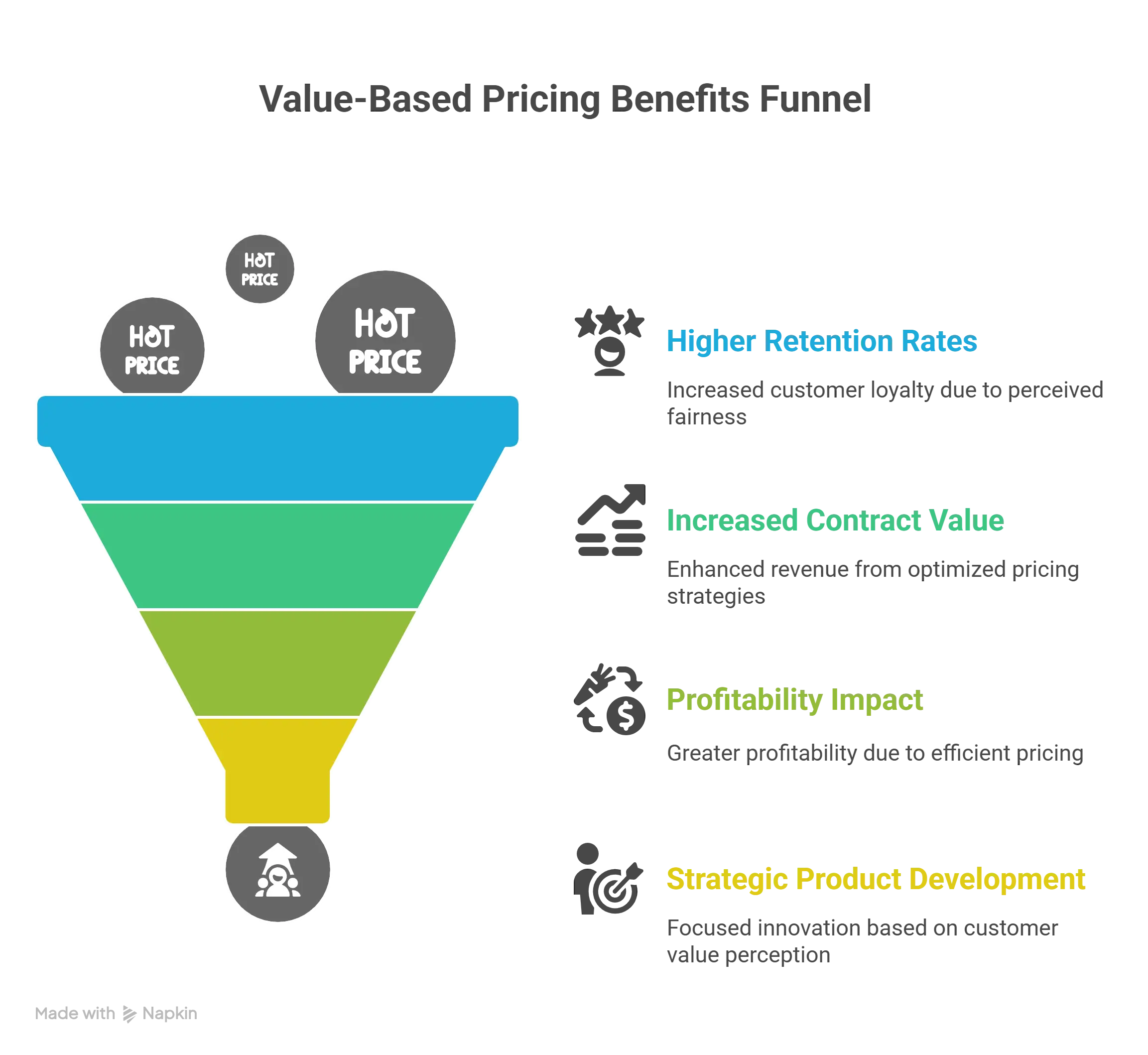
Organizations implementing outcome-based pricing models consistently demonstrate superior business metrics across multiple dimensions. The 15-20% higher retention rates achieved by these companies stem from fundamental alignment between vendor success and customer outcomes. When pricing reflects value delivery, customers perceive fairness that transcends simple cost calculations, creating emotional connections that strengthen long-term relationships.
Contract value increases of 10-15% represent just the beginning of value-based pricing benefits. The profitability impact multiplies because higher prices don’t require proportional increases in service delivery costs. Simon-Kucher & Partners’ research demonstrates that pricing optimization impacts profitability four times more effectively than cost reduction initiatives, making it the highest-leverage growth strategy available to SaaS companies.
Product development gains strategic clarity when pricing aligns with customer value perception. Engineering teams receive clear signals about which capabilities drive willingness to pay, enabling resource allocation toward high-impact features. This product-market fit refinement creates virtuous cycles where better products command higher prices, funding further innovation that deepens competitive moats.
Competitive Differentiation Through Value Alignment
Value-based pricing enables companies to escape commodity pricing pressures that plague feature-comparable competitors. Rather than competing on specification sheets, companies emphasize unique value delivery to specific customer segments. This differentiation strategy proves particularly effective in crowded markets where traditional feature comparisons fail to capture nuanced value differences between solutions.
Customer success metrics improve dramatically when pricing incentivizes vendor behavior that drives customer outcomes. Support teams prioritize high-value activities, product teams focus on impactful features, and sales teams qualify prospects based on value fit rather than simple budget availability. This organizational alignment around customer value creates competitive advantages that compound over time.
Implementation Framework and Best Practices
Successful value-based pricing implementation begins with comprehensive market research that goes beyond surface-level surveys. Companies must conduct detailed customer interviews to understand pain points, quantify business impact, and identify value drivers that influence purchasing decisions. This research should examine how customers measure success, what metrics they track, and how they calculate return on investment from software purchases.
Customer segmentation forms the foundation upon which effective pricing strategies build. Organizations should divide their customer base using characteristics that correlate with value perception and willingness to pay. Enterprise customers typically prioritize integration capabilities, security features, and scalability, while small businesses focus on ease of use and immediate time-to-value. Each segment requires tailored pricing approaches that reflect their specific value drivers.
Developing Comprehensive Buyer Personas
B2B buyer personas must capture detailed information about decision-makers’ roles, responsibilities, and success metrics. Effective personas include obstacles buyers face, vendor selection criteria, budget constraints, and how they measure success post-purchase. These insights guide pricing decisions by ensuring value propositions resonate with specific buyer needs throughout the evaluation process.
Communication strategy development ensures value propositions reach target audiences effectively. Early and frequent customer communication provides insights into messaging effectiveness and pricing receptivity. Companies should introduce value-based pricing gradually, starting with pilot programs that test market response before full-scale implementation. This iterative approach reduces risk while building internal confidence in new pricing models.
Selecting Appropriate Pricing Models
Model selection requires careful consideration of how customers experience and measure value. Tiered pricing works well when value correlates with feature access, while usage-based models suit products where value scales with consumption. Outcome-based pricing represents the most sophisticated approach but requires robust value measurement mechanisms and deep customer partnerships.
Hybrid models increasingly prove most effective, combining multiple value metrics to capture diverse customer needs. Companies might combine seat-based pricing for collaboration features with usage-based pricing for computational resources, creating pricing that reflects how different customer segments derive value. This flexibility enables revenue optimization across heterogeneous customer bases while maintaining pricing simplicity.
Value Metrics and Measurement Strategies
Value metrics serve as the fundamental units upon which SaaS companies build their entire pricing architecture. The choice of value metric shapes business model dynamics, influences customer behavior, and determines revenue scalability. Companies must select metrics that align with customer value perception while enabling predictable revenue growth and operational efficiency.
Per-user pricing, despite its 39% market share, increasingly shows limitations in modern SaaS environments. Organizations often restrict user access to control costs, limiting product adoption and reducing overall value realization. This friction between pricing model and customer success creates opportunities for competitors offering more aligned pricing approaches that encourage broad organizational adoption.
Usage-based pricing models have gained momentum precisely because they remove adoption barriers through pay-as-you-go structures. Companies like Twilio, AWS, and Snowflake demonstrate how consumption-based pricing enables revenue to scale naturally with customer success. The 29.9% five-year CAGR achieved by usage-based models reflects their superior alignment with customer value realization patterns.
Implementing Sophisticated Value Metrics
Outcome-based pricing represents the apex of value-based strategies, directly tying pricing to business results. McKinsey research shows companies using this approach achieve 10-15% higher revenue growth than competitors using traditional models. Success requires sophisticated measurement systems that track customer outcomes, attribute value to specific product capabilities, and create transparent pricing that customers perceive as fair.
Hybrid pricing models combining multiple metrics demonstrate 30% better retention rates according to ProfitWell data. HubSpot’s combination of contacts, users, and feature tiers illustrates how companies can capture value across different dimensions. Salesforce varies pricing by cloud while including data limits, creating flexibility that accommodates diverse customer needs while maintaining pricing coherence.
Measuring and Optimizing Value Delivery
Effective value measurement requires sophisticated analytics infrastructure that tracks customer outcomes beyond simple usage metrics. Companies must identify leading indicators of value realization, such as time-to-first-value, feature adoption rates, and business metric improvements. These insights enable pricing optimization that reflects actual value delivery rather than theoretical benefit assumptions.
Continuous optimization becomes essential as customer needs evolve and competitive landscapes shift. Regular analysis of pricing elasticity, customer feedback, and competitive positioning ensures pricing remains aligned with market realities. Companies should establish quarterly review cycles that examine pricing performance, identify optimization opportunities, and implement incremental improvements based on data-driven insights.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Salesforce exemplifies sophisticated value-based pricing through its tiered approach that aligns feature access with business value delivery. Lower tiers focus on core sales process automation for smaller teams, while enterprise tiers provide advanced analytics, AI capabilities, and unlimited customization that deliver proportionally greater value. This structure enables customers to start small and expand as they realize increasing value from the platform.
HubSpot’s evolution from simple feature-based tiers to outcome-oriented pricing demonstrates how companies can gradually transition to value-based models. The company combines multiple value metrics including contacts, users, and feature access, creating pricing flexibility that accommodates diverse customer needs. This approach has enabled HubSpot to maintain strong growth while improving customer satisfaction through better price-value alignment.
Transformation Success Stories
New Relic’s dramatic shift from per-host to consumption-based pricing represents one of the boldest pricing transformations in SaaS history. The company removed artificial usage constraints that limited customer value realization, initially causing revenue disruption but ultimately enabling stronger customer relationships. This transformation required extensive customer communication, gradual migration programs, and operational changes that aligned the entire organization around consumption-based success metrics.
Slack’s three-tier pricing structure effectively balances simplicity with value differentiation. The free plan limits message history and integrations, creating natural upgrade triggers as teams grow. Standard and Plus plans remove constraints while adding enterprise features, providing clear upgrade paths that align with organizational maturity. This structure has enabled Slack to capture value across the entire market spectrum from startups to enterprises.
Learning from Pricing Mistakes
JustCall’s pricing evolution illustrates how companies can recover from pricing missteps through customer-centric redesign. The company’s initial complex per-user, usage-based model created customer confusion and billing unpredictability. After extensive customer feedback analysis, JustCall simplified to four clear plans tailored to business sizes, resulting in improved satisfaction and more predictable revenue streams.
These case studies reveal common patterns in successful value-based pricing implementation. Companies that succeed invest heavily in customer research, implement changes gradually with clear communication, and maintain flexibility to adjust based on market feedback. The willingness to iterate and refine pricing based on actual customer behavior rather than theoretical models proves critical for long-term success.